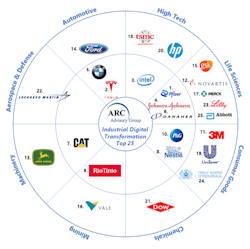
Meet ARC Advisory Group's 2023 Digital Transformation Top 25
ARC Advisory Group has released the second edition of The Industrial Digital Transformation Top 25 report. This report highlights the leading companies that excel at integrating digital technology into all areas of their business, fundamentally changing the way they operate and deliver value to customers.
Digital transformation leaders across many different industries share common traits and visions, helping them overcome complex challenges to innovate and stay agile. Industrial innovation continues to accelerate, and leading companies have their transformation initiatives well underway. For those who succeed, the result is a competitive advantage, even during the most difficult economic times.
With a digital transformation mindset, the core business model by which a company produces and/or offers services to the marketplace can be replaced by new business models that more fully leverage analytics, digital twins, predictive technologies, or other technologies that enable the company to expand their worldview, embrace competitive excellence as a goal, and thereby move beyond production efficiency to a much more dynamic, responsive, and resilient business model.
No single path to digital transformation
The last few years have been particularly challenging ones for industrial growth. We’ve been cornered from all sides: pandemics, political unrest, climate change, and macroeconomic uncertainty. The world as we knew it a few years ago has capsized and the boundaries of the new normal are constantly shifting and realigning. Digital transformation is now an imperative and digital transformation leaders can be found across many different industries, sharing common traits and visions, helping organizations overcome complex challenges to innovate and stay agile.
Transforming to an organization where constant change and adjustment define normal operations is still very conceptual for some industrial companies. While they may have a similar end goal in mind such as competitive excellence, they may have different strategies and tactics, based on their pain points and priorities. One thing is clear: there is no straight line to define the path of a digital transformation journey. Even though some companies may be ahead of their peers, simultaneously they may still be struggling in many areas of their business and operations.
Successful industrial companies modernize their operating practices and technologies to successfully compete in today’s more dynamic and continuously evolving marketplace. Leading companies take a strategic approach, integrating digital technology throughout their value chains. Design and engineering, production operations, maintenance, logistics, supply chain, business systems, customers, products, and organizational structure are subject to innovative change as companies examine and update processes and deploy new tools and technologies.
Focus on asset management
Asset Management is one area that has seen a significant increase in digital transformation in recent years, particularly in the area of maintenance and reliability. With the rise of the internet of Things (IoT) and advanced analytics, asset managers are now able to collect and analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, which has revolutionized the way they approach maintenance and reliability. By using sensors and other connected devices, they can monitor the health and performance of assets in real-time and use predictive analytics to forecast when maintenance will be required. Predictive maintenance helps companies save time, reduce costs, and improve the overall reliability of their assets.
Another key area of digital transformation in asset management is the use of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can be used to analyze larger data sets and identify patterns and anomalies that may not be immediately apparent. By using AI, asset managers can identify potential issues before they become critical and take corrective action before the asset fails. Many of the companies on the DT Top 25 understand how downtime can be extremely costly and recognize digital transformation is improving efficiency, reliability and safety of industrial operations.
The Top 25 industrial companies
The top 25 companies are representative of multiple geographies and industries. Companies in the pharmaceutical & biotech, automotive, high tech, consumer goods, machinery, aerospace, chemicals, energy, and mining sectors are among the leaders (see Figure 1). They share a common thread of leveraging digital technologies to transform business capabilities and outcomes, giving them a competitive advantage during challenging global circumstances.
For this research, digital transformation is defined as: “The integration of digital technology into all areas of business, fundamentally changing the way companies operate and deliver value to customers. The organization is typically charged to innovate and improve across multiple dimensions such as: digital/disruptive technologies, culture and leadership, operational agility, workforce engagement, customer experience, environmental, social and governance, and competitive performance.”
It’s not straightforward to identify leaders in such a complex space, but ARC developed a rigorous process based on financial performance, a community intelligence based ranking system, and software and sustainability data. Publicly available financial information, ARC primary and secondary research, data from ARC’s market database, and the opinions of members of ARC’s community of end users were all factored into the determination of the Top 25 Industrial Companies.
Company profiles
This sampling from the DT Top 25 showcases three companies that have successfully used technology to transform the way they manage operations:
Intel. Intel, a global semiconductor company, combines technology, people, and culture to drive innovation and quality at the production line while ensuring sustainability and safety throughout the business process. Intel’s semiconductor manufacturing process runs 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year.
Digitally transforming its manufacturing operations around connectivity and IoT have fundamentally changed the way Intel runs its day-to-day business—from the types of products and services produced to how they are delivered. While automation has been used for several decades inside the factories, real improvement and transformation has come from the deployment of widespread IoT and predictive analytics at scale, which have demonstrably decreased time to market, improved resource utilizations, increased yields, and reduced costs.
Intel focuses on connecting data insights directly with engineers who can focus on solving problems, with an emphasis on designing solutions instead of extracting data. Digital twin and simulations help optimize the factory output. Even though the company focuses on technology, it is an ecosystem play, not just one technology that delivers a full-blown solution. For Intel, it is the combination of the people, the culture and technology all together, that defines its digital transformation. Intel is also committed to corporate responsibility and sustainability throughout their entire business.
Caterpillar. Caterpillar is a leading manufacturer of construction and mining equipment, diesel and natural gas engines, and industrial gas turbines. The company has embraced digital transformation using technologies such as IoT, data analytics, and AI to improve the efficiency and productivity of its operations.
In the area of transportation, Caterpillar has implemented various digital initiatives, such as the use of telematics systems to track and monitor its fleet of vehicles, as well as the development of autonomous vehicles for use in its operations. In addition, Caterpillar has invested in the development of digital tools and platforms to improve the maintenance and repair of its transportation equipment, including the use of predictive analytics and machine learning to identify potential issues before they occur.
The company looks at its digital transformation as a journey comprised of five key steps: Drive digital transformation from the top; define digital vision; develop a digital strategy; create a digital roadmap; and build a digital organization structure.
Eli Lilly. Eli Lilly’s core business is the discovery, development, and manufacture of pharmaceutical products. Through its history, Lilly has prided itself for its innovative research, corporate responsibility, and contributions to the pharmaceutical industry.
They see the digital plant as a way to accelerate improvements. For example, the company reduces ergonomic risks by using robotics for lifting boxes and ensures quality through real-time analytics rather than after-the-fact testing. These technologies also drive cost efficiencies. Additionally, Eli Lilly has been investing in technologies such as blockchain and digital twins to improve supply chain traceability, logistics and inventory management, and quality and regulatory compliance.
The digital plant and technologies that go along with digital transformation, such as robotics, data analytics, AI, and the industrial Internet of things (IIoT), promise greater efficiency. Eli Lilly has been advancing in applying these technologies to its pharmaceutical manufacturing organization, which the company claims has enabled it to make better medicines. The company established a role dedicated to corporate global reliability, which involves helping silos to communicate, making them more comfortable, not always leading but at least interacting.