Damaged filler metals — including stick electrodes and solid or tubular wire — can cause poor weld quality that ultimately leads to expensive and time-consuming rework. If filler metals become wet or pick up contaminants, such as dirt, oil or grease, they need to be replaced. That replacement leads to three costly problems. First, it causes downtime for changing over the filler metal, particularly welding wires. Second, filler metal damaged by the environment almost always voids most industry-standard one-year warranties on the product. And finally, it costs you money, both for the price of the ruined filler metal and for the purchase of new filler metals.
Taking some simple precautions, however, can ensure that you are storing and handling your filler metals correctly — and getting the best performance from them.
Damage control
When filler metals leave the factory, they are sealed (usually vacuumed, hermetically, and/or placed in a heavy plastic bag or wrap). They are also in the best possible condition for the job. Regardless of the conditions of your facility, it is important for you to keep them that way. Fortunately, there are some relatively easy steps you can take to help them accomplish this task.
First, you should always use gloves when handling filler metals. Solid wire, in particular, can easily pick up sweat from bare hands. This moisture causes rust to form on the surface of the wire, which, in turn, leads to poor wire feeding and may create porosity in the finished welds. You can usually tell through a visual inspection of solid wire if it has been damaged in this way; the rust mark will often be in the exact shape of a handprint. Other types of filler metals won’t show such telltale signs of improper handling, but it is nonetheless important to wear gloves when removing them from their original packaging or preparing them for welding.
[pullquote]If you use plasma or oxyfuel cutting systems in your facility, be aware that these can create a significant amount of dust. You should keep your filler metals away from areas where these processes occur, as the cutting dust can accumulate on the surface of solid and tubular wires, and cause poor wire feeding. The cutting dust can also clog the contact tip and nozzle in these applications, creating poor electrical conductivity and an unstable or erratic arc. In a stick electrode application, dust can lead to weld porosity.
You should also keep filler metals away from water, oil, grease or other similarly damaging elements. These contaminants can all lead to poor weld quality, rework and/or welding performance issues. Moisture, especially, can cause hydrogen-induced cracking that must be repaired.
The single most important practice you can implement, however, is to store filler metals properly when they are not in use. At a minimum, you should cover the welding wire spool with a plastic bag if you plan to leave tubular or solid welding wire on the feeder overnight. A better practice is to remove the spool from the wire feeder, place it in a clean plastic bag and close it securely. Then place the secured package into the original box and store it in a clean, dry area until it is ready for use again. Both practices help protect against contaminants.
Using an enclosed wire feeder, when possible, is also a good way to protect the welding wire from the environment. Still, this type of feeder will not prevent damage to the filler metal surface if the welding wire is left in the enclosed feeder for any length of time. You should still follow proper handling storage procedures.
Stick electrodes also require proper handling and storage in order to provide good weld quality, maintain compliance with the specified welding parameters and eliminate unnecessary downtime.
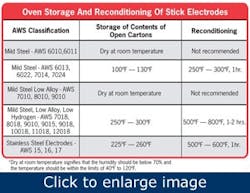
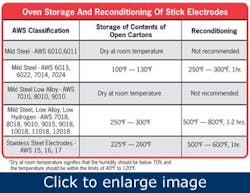
Without question, moisture is the number one enemy of stick electrodes. It can cause hydrogen-induced cracking, porosity and a host of other weld discontinuities that require rework. Depending on the type, stick electrodes must often be stored in a holding oven at a specific temperature (See Figure 1) to protect them from moisture. In some cases, a specific welding procedure or code dictates how long a package of stick electrodes can remain open before it must be discarded — regardless of whether it has been stored in an oven or not.
Not surprisingly, leaving a package (can or carton) of stick electrodes open and/or storing it improperly can be damaging, especially with low-hydrogen products. You should always follow the welding code specifications for the job, as well as the filler metal manufacturer’s instructions for the particular stick electrode. Proper oven storage and holding temperature are key. You should also look for packaging options that provide greater moisture resistance, such as a wax-coated carton or plastic package, and always close the package after retrieving an electrode.
In the event that stick electrodes have been exposed to moisture, you should follow the recommended procedures for reconditioning them. Reconditioning involves placing the damaged electrodes in an oven at a given temperature for a specified period of time. Instructions for reconditioning are included with the original stick electrode package, or can be determined by contacting a trusted welding supply distributor. Welding wires should never be reconditioned.