Conflict in the workplace is very destructive. It makes people reluctant to work together. But what causes conflict? The simple answer is that conflict happens whenever two parties don’t see eye-to-eye.
During everyday activities, conflict comes from ambiguity, gaps, and overlaps in roles and responsibilities among individuals and work centers. If there is urgency, such as when production is disrupted because of equipment failure, conflict is generated by differences in objectives. Operations wants the system up immediately. Maintenance folks want time to repair the system so that it will not soon fail again.
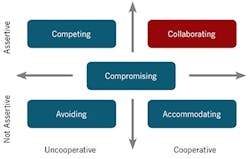
How do you develop guidance or resolve conflict in a way that brings people and work centers together? The first thing to do is to understand conflict management styles. Conflict management styles can be thought of relative to their position on two dimensions.
The first dimension is the extent to which the first party is assertive and satisfies its own concerns. This is shown in the vertical axis in Figure 1. Toward the low end of the axis is a lack of assertion – ultimately, submissiveness. Toward the high end is assertion, and ultimately aggressiveness. The second dimension is the extent to which there is cooperation with the other party, represented by the horizontal axis.
Within the scope of the assertiveness and cooperation axes, there are five styles for conflict management: