Starting a vibration-based PdM program doesn't have to be traumatic
Establishing a vibration-based predictive maintenance (PdM) program at your plant doesn’t have to be a traumatic experience
The main concern is to establish a program that’s cost-effective. A program that costs more to operate than it saves in unscheduled downtime is not an effective tool.
The purpose of a vibration PdM program is to limit the amount of unscheduled downtime and to detect and remedy problems before they cause extensive damage to machines or personnel.
Developing a machine list
The first step in initiating a PdM program is to develop a list of machines critical to the operation of your facility. Note that these machines are not necessarily the largest or most expensive machines.
The most successful PdM programs start small and grow. This allows the system to begin working without overwhelming the maintenance staff with its findings. During the initial start up, the number of problems found in machines will likely be high, especially for the older ones.
The machine list should be a detailed list and include the name and type of machine, as well as related components, such as the gearbox, bearings, couplings, sheave sizes, belts and the base used (grout or springs). This information will be helpful when constructing the database and analyzing vibration data.
Outsource or in-house?
Now that the comprehensive critical machine list has been fine-tuned, it’s time to make an important decision that is crucial to the start of an effective program. It’s whether to administer the program in-house or with an outside vibration consultant.
When doing the program in-house, there are many factors to consider. One is what level in the corporate structure will the program reside. This must be determined early on because it involves the management of the program as well as data collection and analysis. Another concern is acquisition cost equipment and selection of data collectors and condition monitoring software. However, the most important decision relates to the personnel that will be trained to operate the equipment and manage the program. Several employees should be trained in the use of equipment to prevent the program from failing because of personnel changes.
What equipment to purchase
The equipment purchase decision should not be made on price alone. Take a good look at the equipment and available support in your area. It’s a good idea to talk with service providers and see what they use. Data collectors and software packages are similar and differ mainly in the bells and whistles.
The most common type of data collectors use the Fast Fouirer Transform method of processing data, which works well with a vibration PdM program. The software package should be capable of trending, as well as be compatible with your current computer system. Purchase a software system that’s been around awhile and has had the bugs worked out. It also might be best to use the same data collectors and software as one of the local service providers. This provides a second source of assistance besides the sales rep who sold you the equipment.
Take full advantage of training offered by your vendor. Also consider training from a local service provider or user groups. There also are professional associations that offer educational courses and proficiency tests.
Outside vibration consultants
If an outside consultant will administer the program, the local service providers should be considered. They should be invited to your facility to make a presentation of their services and asked to provide a quotation based on your machine list. Other services they provide to accompany the vibration program should also be considered in this process. Most service companies tend to keep up-to-date with the latest equipment and software and have highly trained personnel in database setup, data acquisition and data analysis. During their presentation ask to see an example report from other programs.
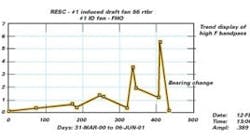
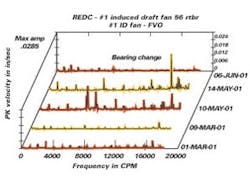
Vibration spectrum trended over time. This shows before and after the bearing was changed.
When the consultant prepares a report for your facility, it should be concise, easy to understand and include recommendations as to how to repair any machines having faults. If the report structure doesn’t meet your needs, then address this situation with your consultant. It should be possible for the report to be customized for your needs.
Database construction
The next crucial step is constructing the database. It should be setup to optimize the capabilities of data acquisition equipment and software.
Information collected on the machine list should be exported to the database. Take the time to fully incorporate bearing and gearbox information. Many software packages allow you to input bearing and motor information, including automatic fault detection setpoints.
If you have variable-speed or variable-load equipment, make sure your software accommodates this information. Machine rotational speed is the key to data analysis.
Database hierarchy
Trend data from an alarm band
The databases are constructed in a tree type fashion. The database is divided into routes, which are, in turn, delivered to specific machines. The machines receive multiple monitor points, with each monitor divided into multiple analysis parameters. The number of parameters available depends on the software package, but it’s usually between six and 12. Each analysis parameter has a frequency range based on specified fault requirements. They also are given an alarm and alert value.
Setting parameters
Until a good baseline is established, the database is often set up using standard analysis parameters and alert values provided by the software package. Parameters can be adjusted to capture the required frequency range. Alert values can be established to prevent false alarms, while still providing adequate warning on machine conditions.
For most machines, the data base parameters should be set to capture at least one high-frequency parameter for each monitoring point. This information is crucial in early detection of gear and rolling-element bearing faults. Databases also should be set up to save both vibration spectrum and time waveform results.
Measurements locations
The monitoring points should be setup so that the measurement is recorded at or near the location of the bearings. A critical element of the PdM program is its ability to make repeatable vibration measurements. Points should be marked on the machine and, in some instances, targets may need to be installed. Vibration monitoring locations and type of vibration sensor mounting depends on the machine being measured and the vibration frequency range.
One popular measurement tool is an accelerometer, which can be mounted with a high-strength magnet. In some cases, other measurement tools or mounting devices are needed. Vibration measurements should be recorded on structurally sound areas of machines. They should not be recorded on the endbells of motors or at any location that tends to amplify the vibration and trigger false alarms.
Data acquisition and processing
Once the database is setup and downloaded to the data collector, the technician can then go to the machines and perform the data acquisition function. It’s important to view the data during collection to ensure its quality. Make sure the spectrum is clear and there is not significant low- frequency noise. If the data is bad, simply collect it again at the same point. After the data has been collected, it’s downloaded to the host computer where it can be viewed, analyzed, manipulated and trended.
Machine condition report
The vibration analyst in charge of the program should then analyze the data and issue a report on the findings. Even in an in-house program it is a good idea to provide a report and a machinery status list to give to the maintenance staff and management. This way, the full value of the program can be seen by everyone involved.
Maintaining the PdM program
When the program is up and running, the database will need be modified for changes in machinery or monitoring parameters. Just like a well-oiled machine, PdM programs require a little maintenance and adjusting from time to time to keep them operating in a smooth and efficient manner. Initially, the staff should concentrate on maintaining the vibration program and not be too concerned about processes such as dynamic balancing until they are comfortable with the program and its equipment. During the early stages keep local service providers involved to provide assistance with certain pieces of equipment and for dynamic balancing procedures. After full implementation, it’s time to train the personnel in the art of dynamic balancing.
Consultants may also be needed from time to time to assist with a complex machine diagnoses or when the program has missed a few failures. If the PdM program is missing failures, an evaluation should be done using root cause analysis. For example, a measurement point frequency may need to be adjusted.
There are times when even a well managed program will miss something and a machine failure occurs. These situations can be limited by augmenting the vibration based technology with other PdM technologies such as thermography, oil analysis, motor circuit testing and ultrasonic testing.
Remember, PdM programs are another tool to be used in preventing machinery failure and are only as effective as the people involved with the program.
Graphics: Lindskog Balancing